What is a Sitemap?
As the name says, it’s a map of your website. Sitemap contains a list of all URLs your website has and Magento sitemap isn’t an exception. It helps search engines to find trails to all your pages and make sure your website is indexed and pages are crawled correctly.
Sitemaps can be in different formats: XML sitemap, RSS or Atom. The important difference is that RSS/Atom feeds describe recent changes while XML sitemap includes all website URLs. In this post, we are going to speak about XML sitemap.
Why Do You Need a XML Sitemap?
Sitemap helps search engines to find and better understand all content presented on a website. A website doesn’t need to have a sitemap to get indexed. If a website has a proper structure, hierarchy and all pages can be reached in four-five links of the home page, it’s unlikely that any indexation problems occur. Nevertheless, a proper sitemap makes search engine’s job easier by helping them discover and index new content faster so it’s considered good practice to have one.
Another argument for creating a sitemap is that modern SEO is “content-oriented”. Sure, content quality is still a top priority and should be done right, but the frequency of content updates also matters. Search engines value new content, but what they value even more – frequently updated and expanded content. And sitemap does a great job in letting search engines know about recently updated content.
XML Sitemap Elements and Definition
Most of sitemaps look like this:
As you can see, sitemap includes specific tags that “explain” the provided content. Some of them are required and some are optional.
Required:
<urlset> It’s the main sitemap container. It “Encapsulates the file and references the current protocol standard.”
<URL> Serves as a parent tag for each URL entry and is a parent tag for all remaining tags.
<loc> Each URL goes inside this tag. URL must begin with the protocol (such as http) and end with a trailing slash, if your web server requires it. Can’t exceed 2048 characters.
Optional:
<lastmod> The date when the page was modified the last time. Should be in W3C Datetime format.
<changefreq> How frequently the page is likely to change. This is just a recommendation for search engines. The actual crawl frequency may correlate. Valid values:
- always
- hourly
- daily
- weekly
- monthly
- yearly
- never
<priority> Tells search engines how important the URL (page) is compared to other pages on your website. Valid values range from 0.0 to 1.0. The default value is 0.5.
Magento Sitemap Best Practices
- Crawl your website before creating a sitemap. Make sure that you don’t have broken pages and duplicate content. To find crawl errors you can use Google Webmasters Tools (go “Crawl”-“Crawl Errors”).
- If you have lots of webpages, only include the most important ones. Keep in mind that XML Sitemap has a limit of 50,000 URLs or a 10MB in size (uncompressed).
- Don’t include URLs that can’t be fetched by Google. It’s a common mistake to include URLs that are blocked in robots.txt or don’t even exist (404).
- Include only canonical (main) URLs. Don’t include both versions with “WWW” and without, simple products that exist only in a form of one configurable product, etc. This won’t improve indexation but only increase the load on the server.
- If your site is relatively small and changes regularly, update the XML sitemap once a day and ping Google after you update it.
- Avoid too many XML Sitemaps per site. If you have several sitemaps, it’s recommended to create only one sitemap index file which includes all sitemap files and sitemap index files.
- Include the path to your sitemap in robots.txt files and add the sitemap location in search engines’ Webmaster Tools.
- Update modification time only in case the content was changed meaningfully. Also, don’t set the current time when sitemap is served as the last modification time.
How to Create Magento Sitemap
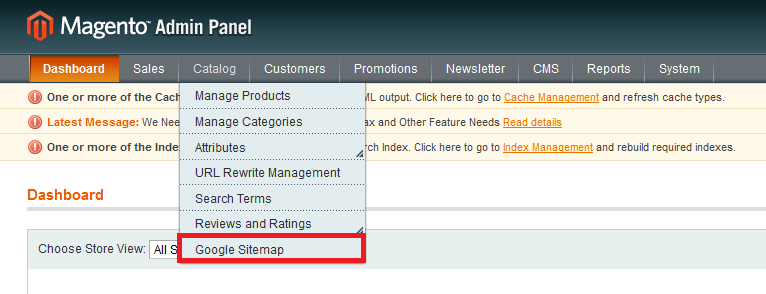
Magento lets you easily create XML sitemap by default. If you are using Magento 1, go to Catalog > Google Sitemap > Add Sitemap.
If you are using Magento 2, go to Marketing > SEO and Search > Site Map.
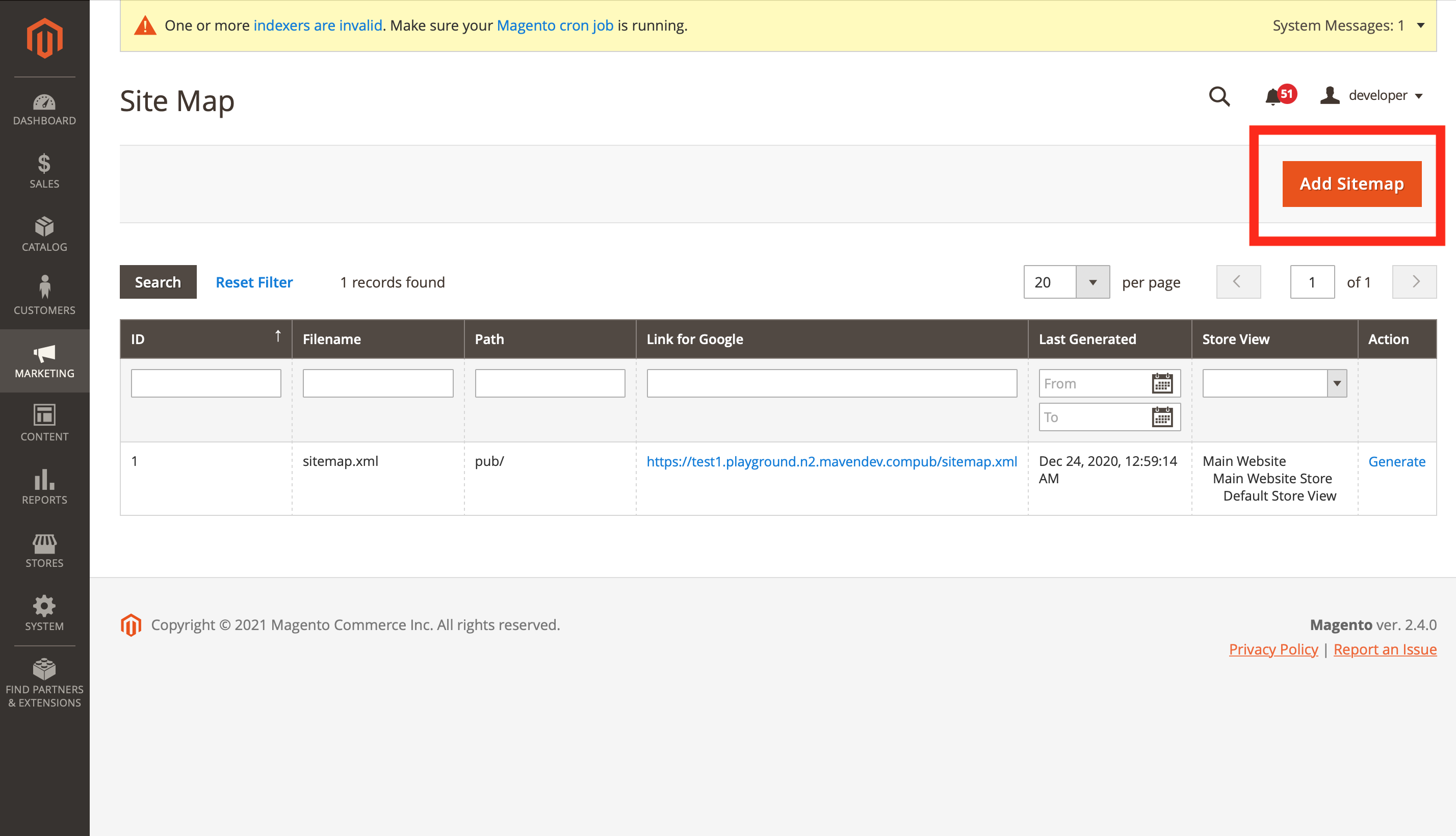
Further, no matter which version of the Magento you are using, you have to fill the following fields:
→ Filename – the name of your sitemap. The best practice is to name it “sitemap.xml“.
→ Path – how the sitemap can be found. To make sure your sitemap is easy to find use ”/”. In such case, sitemap will be accessible at http://example.com/sitemap.xml
→ Store view – if you have several store views, you can separate their sitemaps and generate a different sitemap for each store view. (Only available in Magento 1.x)
Now click “Save” or “Save & Generate” in the top right corner.
In case you click “Save” button, your sitemap won’t be generated until you click “Generate” on the right side of your sitemap name.
That’s it, your Magento Sitemap is ready.